BIOSCIENCE Pathological specimen preparation/pathological examination
Pathological specimen preparation/pathological examination
Our company was determined as “compliant” in a GLP compliance review by the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency in 2018 on partial outsourcing (pathological tissue specimen preparation) of GLP applied study for drug product, medical device, and Regenerative medicine. We will continue to strive to further improve the quality of our specimens as a GLP facility.
Bioscience Business Division / Contract Study Department / Pathological Group, offer pathological tissue specimen preparation (necropsy, trimming, embedding, sectioning, staining/sealing) and histopathological examination. We provide preparation of H.E. staining, special staining, and immunohistochemical staining sections. In addition, we provide ground specimens of undecalcified hard tissue as well. A large variety of staining methods will be conducted according to customer needs. Please feel free to contact us.
Histopathological specimen preparation
Delivered tissue, fixed with 10% neutral buffered formalin or 4% paraformaldehyde, will be trimmed into optimal sizes, so that the target area can be observed (trimming).
The trimmed tissue will be dehydrated and embedded in paraffin to prepare paraffinized block specimen This paraffinized block will be thin sectioned into 1 to 10 μm thickness according to the objective. Staining the sectioned samples will complete the histopathological specimen.



Ground pecimens of undecalcified hard tissue
Here is an interview with one of our membersregarding histopathological specimen (ground specimens) preparation.
Here is the machine used in the video (BS-300CP).
* Access Product page of MEIWAFOSIS CO., LTD.


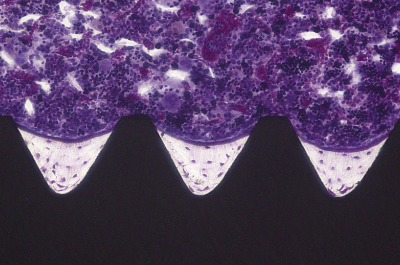
When a hard tissue such as bone or teeth is to be measure bone morphometry, hard tissue will be prepared without decalcification (undecalcification), embedded in resin, thinly polished, and stained (ground specimen).
Preparation of ground specimen is possible from tissue implanted with medical device, within or surrounding the tissue, made from metal and ceramic materials that are difficult to conduct histopathological specimens.
In addition, preparation of specimen for medical device GLP study is possible.
- [MMA resin]
- •Hematoxylin-eosin stain (H.E. stain)
- •Villanueva Goldner stain
- •Villanueva Bone stain
- •Toluidine blue stain
- [Technovit resin]
- •Hematoxylin-eosin stain (H.E. stain)
- •Immunostaining (CD45)
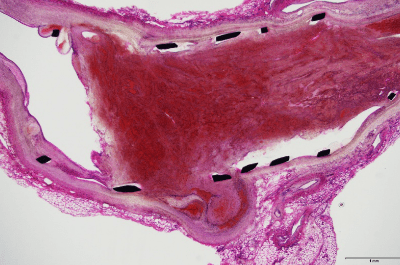
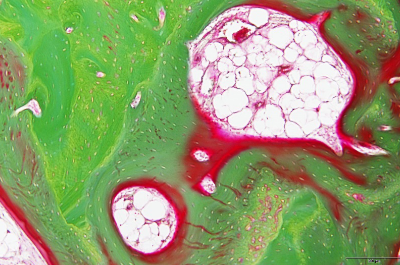
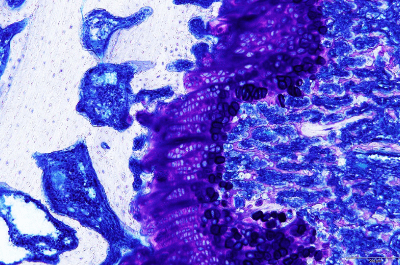
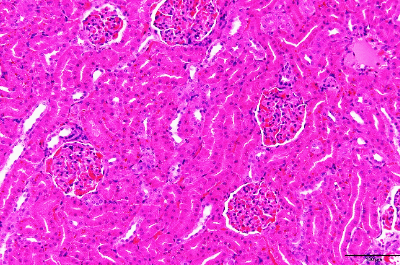
Hematoxylin-eosin stain (H.E. stain) specimen
H.E. staining is the most commonly used stain in histopathological examination.
Even though many types of special staining or immunohistochamical staining methods to detect specific substances are being developed rapidly, H.E. staining is still always being conducted as routine staining.
Hematoxylin, a basic dye stains basophilic structures: nucleic acid. Eosin, an acid dye counterstains basic elements: cytoplasm, RBCs.
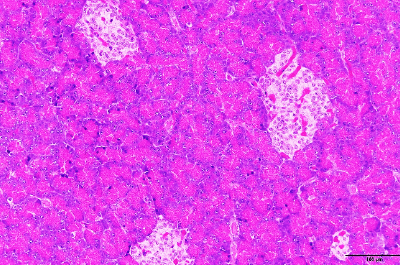
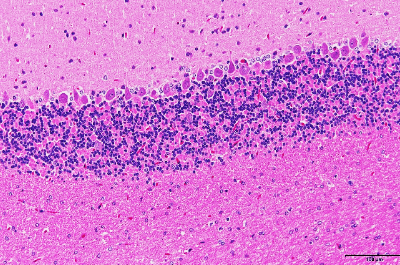
Special staining section
Special staining contains abundant methods to detect specific substances (protein, polysaccharides, and lipid, etc.) and metals (calcium and zinc, etc.), each.
Please feel free to contact us, also about stainings not listed..
- [Connective tissue stain]
- This can be used in a wide variety of applications such as observation of fibrosing lesion and basement membrane.
| Masson's trichrome (MT) stain | Collagen fiber will be stained in blue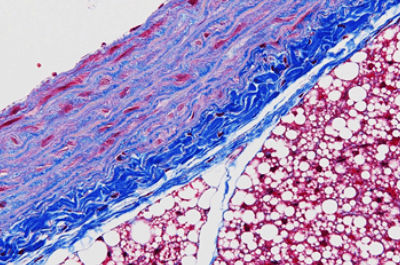
|
|---|---|
| Sirius Red stain | Muscle fiber, collagen fiber will be stained in red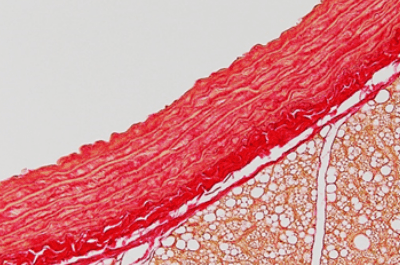
|
| Elastica‐van Gieson (EVG) stain | Elastic fiber will be stained in black purple, collagen fiber will be stained in red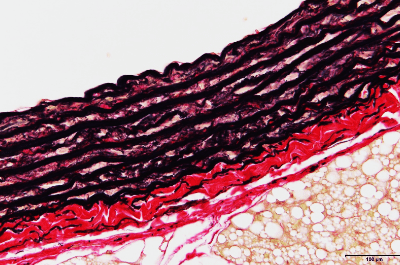
|
| Azan stain | Due to pigment penetration difference, collagen fiber, reticulum fiber, and hyaline droplet will be stained in blue, and fibrinogen will be stained in red. It is also used to differential staining of A, B, and D cells and intracellular granule of the pancreatic islet. 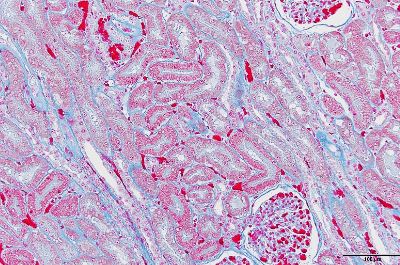
|
| Elastica-Masson stain | Elastic fiber will be stained in black purple, collagen fiber will be stained in green, smooth muscle cells and muscle cells will be stained in red-orange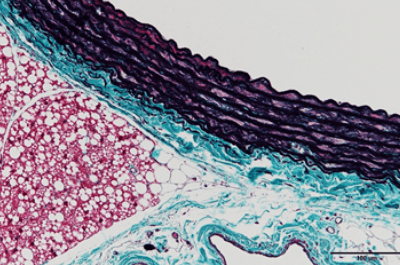
|
| Watanabe‘s silver impregnation (Ag) method | Reticulum fiber will be stained in black, collagen fiber will be stained in red-purple |
| Phosphotungstic acid hematoxylin (PTAH) stain →DIC, collagen disorder, striated muscle, gliacyte, etc. |
Fibrinogen will be stained in blue |
- [Polysaccharides stain]
- This staining is used to observe glycogen, epithelial adenocarcinoma, and fungi, etc.
| Periodic acid Schiff (PAS) stain → Epithelial adenocarcinoma, fungi, entamoebic histolytica, etc. |
Intracellular glycogen will be stained in red to red-purple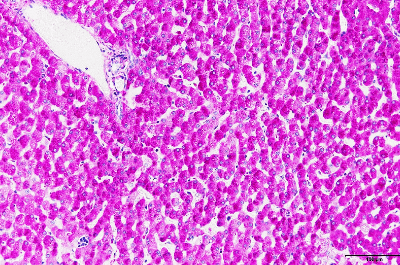
|
|---|---|
| Toluidine blue (Tb) stain →Mastocytoma, etc. |
Due to metachromatism, mast cell granule and acid mucopolysaccharide will be stained in purple.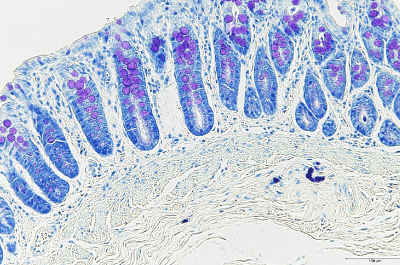
|
| Alcian blue (Al-b) stain →Cartilage, cryptococcosis capsule, etc. |
Acid mucopolysaccharide such as mucin and proteoglycan will be stained in blue. |
- [Nerve tissue stain]
- It is used to observe demyelination lesions, nerve cell forms, etc.
| Luxol fast blue stain → Demyelination lesion, etc. |
Myelin sheath will be stained in blue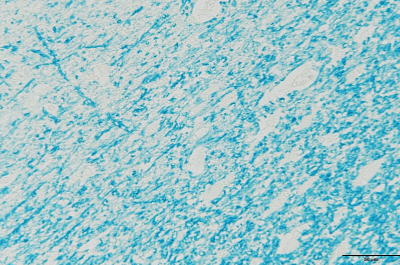
|
|---|---|
| Nissl stain | Nissl body will be stained in red |
| Klüver-Barrera (KB) stain → Demyelination lesion, etc. |
Combination of Luxol fast blue stain and Nissl stain will cause myelin sheath and Nissl body to be stained in blue and red-purple, respectively |
- [Basement membrane stain]
- Used to observe renal glomerulus basement membrane, mesangium cells lesion, etc.
| Periodic acid-methenamine-silver (PAM) stain | Renal glomerulus basement membrane, mesangium cells, renal tubular basement membrane, and epithelial basement membrane will be stained in black.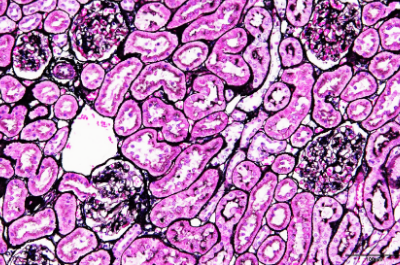
|
|---|
- [Blood cell stain]
- It is used to observe bone marrow lesion, blood diseases, etc.
| Giemsa stain → Bone marrow, blood smear, etc. |
Red to blue staining according to acidophilic to basophilic of the blood cell granule. * Applied to not only biopsy and smear, but also with bone marrow tissue specimen 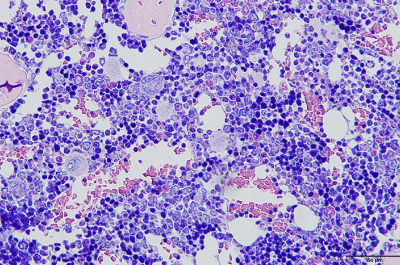
|
|---|
- [Fat tissue stain]
- It is used to certification of fat which cannot be done in ordinary paraffin section, such as fat accumulation.
* Preparation of frozen section is needed
| Sudan III stain | Unlike scientific pigment binding, which transfers water-insoluble alcohol pigment from organic solvent to fat in a constant distribution ratio causing fat to stain in red, this is a physical stain method. |
|---|---|
| Oil red O stain | The principle is the same with Sudan III, however, pigment is more hydrophobic, and fat stains in more prominent darker red. |
| Sudan black B stain | As with the above 2 stain methods, fat will be stained in black, and phospholipid and free fatty acid will be stained in black at the same time. |
- [Cartilage tissue stain]
| Safranine O stain | Cartilage will be stained in red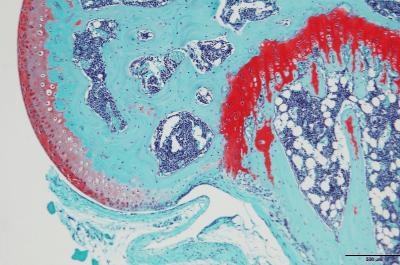
|
|---|
- [Amyloid stain]
- Amyloid deposit in Amyloidosis, Alzheimer's disease, etc.
| Congo red stain | Pigment will enter within β sheet structure of amyloid causing amyloid to be stained in red. * Green under a polarizing microscope * Samples soaked in formalin for a long term will be less likely to stain |
|---|
- [Argyrophilic stain]
- It is used to differentiate carcinoid tumor, melanin, and lipofuscin, as well as Cryptococcus.
| Fontana-Masson stain | Silver ion within ammonia silver solution will be reduced by the cell itself and will be stained in black |
|---|
- [Inorganic salt stain]
- It is used to observe metabolism abnormality, intoxication, and hemolytic anemia, etc.
| Berlin blue (Fe) stain → Sideroferous cells in hemolytic anemia, heart disease cells, etc. |
Pigment will bind with trivalent iron ions in hemosiderin to make Berlin blue and causes blue stain |
|---|---|
| Kossa (Ca) reaction | Calcium salt within the tissue will change into silver salt by silver nitrate and will be reduced, resulting in black staining. |
- [Tartaric acid resistant acid phosphatase stain]
- It is used to observe osteoclastic cells, epiphyseal cartilage cells, and foreign-body giant cells and to differentiate tumors.
| TRAP stain | Tartaric acid resistance acid phosphatase activity, which remains active under the presence of tartaric-acid, is observed in red.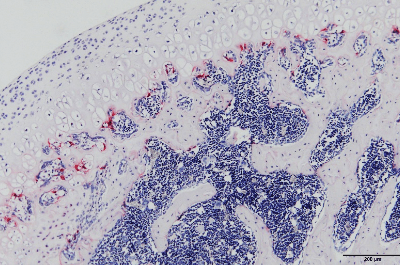
|
|---|
Immunohistochemical staining section
There are enzyme immunoassay and fluorescent antibody methods in immunostaining.
Enzymatic immunohistochemical stained sections will be a permanent specimen; however, immunofluorescence histochemical stained section will not be permanent because fluorescence intensity will decrease, although it has vibrant colors. Immunohistochemical staining is usually applied to paraffin section or unfixed frozen section, and is widely used for detecting cell surface/intraceller antigen, hormone, PCNA and BrdU for mitotic cells, apoptosis, and receptors, etc.
Our group offers Enzymatic immunohistochemical staining according to each study.
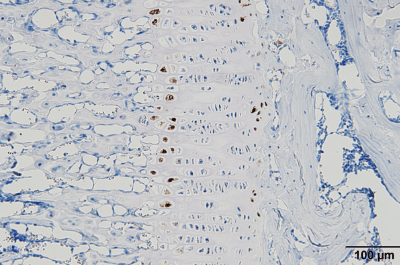
Histopathological examination
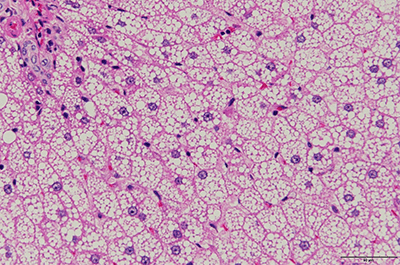
Pathologists who are experts on toxicologic pathology will conduct histopathological examinations such as safety study, exploratory toxicity study, and efficacy pharmacology, etc. In efficacy pharmacology, assessment criteria of the histopathological changes of pathological model [knee osteoarthritis (OA), atopic dermatitis (AD), pulmonary fibrosis (PF), experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), glomerulonephritis (GN), and carcinogenesis, etc.] will be established based on references to determine grades, and quantitative assessment of pathological findings using image analysis will be conducted as needed.
[ close ]
